Describe Alternation of Generations in Plants
It produced eggs n in the archegonium. Alternation of generations is a common factor in plants algae and fungi.
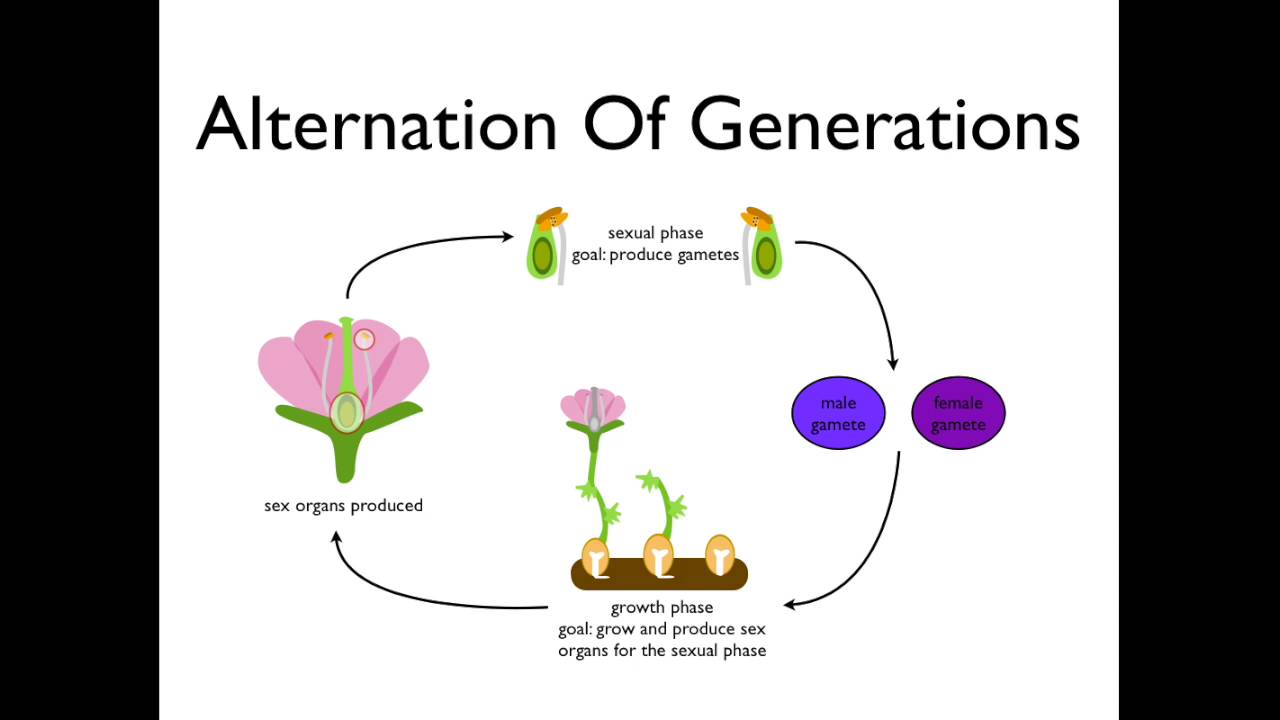
Alternation Of Generations Angiosperms Youtube
The alternation of generations is an important concept in the evolution of flowers.

. The sporophyteThe other form is haploid with only one set of chromosomes. Each is called one generation. A multicellular gametophyte which is haploid with n chromosomes alternates with a multicellular sporophyte which is diploid with 2n chromosomes made up of n pairs.
The multicellular haploid plant structure is called the gametophyte which is formed from the spore and give rise to the haploid gametes. Answer and Explanation. The two generations or life cycles that occur are called the sporophyte generation and the gametophyte generation.
Alternation of generations is a term primarily used to describe the life cycle of plants. All land plant life have alternation of generations. Binary fission The life cycle of all plants includes an alternation of generations that features haploid 1n gametophytes and diploid 2n sporophytes.
In sexual reproduction organisms have a haploid phase with one set of chromosomes and a. Alternation of Generations This term refers to the life cycle of most plants in which the generations alternate between haploid gametophytes and diploid sporophytes. A general form of alternation of generations looks like this.
Plants alteration of generation mean occurrence of conversion of gametophytic stage and sporophytic stage on each other and their dependency in plant life cycle. Hence the whole mechanism is called alternation of generations. Meiosis In plants both the diploid and haploid stages of the life cycle are sporophyte gametophyte The diploid stage produces develop via female via which into the haploid stage which produces male and antheridia es Male gametangia called.
Depending on the type of plant these two phases may be similar or very different. The fluctuation between these diploid and haploid stages that occurs in plants is called the alternation of generations. In bryophytes mosses and their ilk the gametophytes are the bigger generation but in other land plants sporophytes are bigger.
It is not always easy to observe however. The dominant plant is a diploid sporophyte which forms haploid spores. As plant groups have evolved complexity from bryophytes moss to angiosperms.
The term alternation of generations is used to describe an alternation of forms in the life cycle of plants and some protists. One form is diploid with 2n chromosomes. Bryophyte has haploid gametophyte dominant body.
Do meiosis These egg and sperm gametes undergo fertilization to form a diploid 2n zygote that develops into a. During the course of their life cycles plants alternate between two phases. The sexual generation in plants produces gametes or sex cells and is called the gametophyte generation.
The gametophyte generation is the phase that produces gametes or reproductive cells egg. The gametes fuse to form a zygote that develops into a sporophyte. This is called alternation of generations.
The two phases or generations are often morphologically and sometimes chromosomally distinct. Alternation of generations also called metagenesis or heterogenesis in biology the alternation of a sexual phase and an asexual phase in the life cycle of an organism. The forms that the sporophytes spores gametophytes and gametes take on vary depending on the type of plant.
Alternation of generations is seen in both vascular and. There is a rotation between these generations. Alternation of generations describes a plants life cycle as it alternates between a sexual phase or generation and an asexual phase.
All plants exhibit a phenomenon called alternation of generations. Alternation of generations refers to the occurrence in the plant life cycle of both a multicellular diploid organism and a multicellular haploid organism each giving rise to the other. It is a complex cycle with many different life stages that can be be both diploid and haploid.
All land plant life have alternation of generations. They germinate on the ground into a gametophyte which produces haploid male and female gametes. Complete the following statements to explain the differences in the alternation of generations of land plants.
Alternation of Generations Plant vs Animal Life Cycles. So one complete life cycle of a plant includes two generations that alternate with each other. In some plants sporophyte 2n is dominant whereas in some plants gametophytic n is dominant.
Alternation of generations is sexual reproduction in plants as it involves the creation and combining of sex cells. The sporophyte generation is the phase that produces spores. The asexual phase produces spores and is called the sporophyte generation.
In algae fungi and plants alternation of generations is common. In mosses and their household bryophytes the haploid gametophyte is the dominant technology and the diploid sporophytes are sporangium bearing stalks growing from. Diploid 2n Plant gametophytes utilize the process of mitosis to produce eggs and sperm.
Alternation of generations can be defined as a type of life cycle in which a number of generations of plants differentiate between diploid and haploid organisms. The life cycle of a plant is called the alternation of generations. All embryophytes and some algae undergo this process.
The gametophyteBoth forms are multicellular. Plants and some animals are capable of reproducing both asexually and sexually. This is in contrast to animals in which the only multicellular phase is the diploid organism such as the human man or woman whereas the haploid phase is a.
Plant life cycle and alternation of generation.

Alternation Of Generations Plant Definition Life Cycle Biology Dictionary
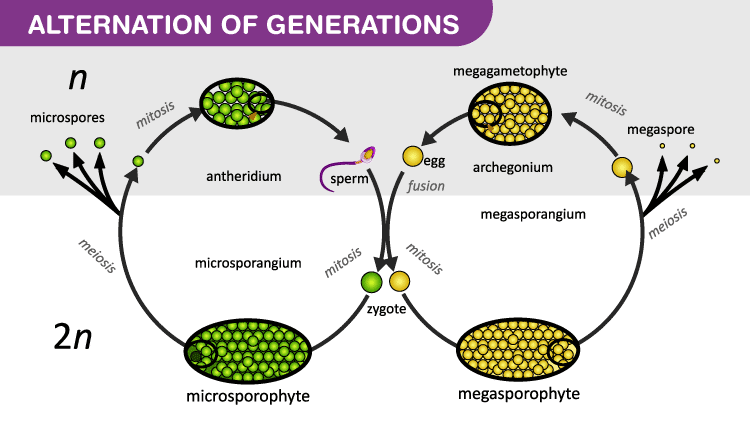
Alternation Of Generations Life Cycle Of A Plant

Alternation Of Generations Simple English Wikipedia The Free Encyclopedia
Comments
Post a Comment